Seattle, WA
(206) 571 7580
Kent, WA
(425) 440 0966
Kirkland, WA
(425) 200-8045
Renton, WA
(425) 495-1903
Redmond, WA
(425) 495-0306
PROTECT BUSINESSES AND FAMILIES IN THE LOCAL COMMUNITY
Seattle, WA
(206) 571 7580
Kent, WA
(425) 440 0966
Kirkland, WA
(425) 200-8045
Renton, WA
(425) 495-1903
Redmond, WA
(425) 495-0306
Exterminators Say Goodbye to Ant Infestations Today!
Expert Commercial Ant Extermination Services in Seattle & King County Surrounding Areas
Fast & Effective Ants Control Service Near Me
Don’t let ants take over your home or business. Local Commercial exterminators ensure swift and efficient removal of all ant types, from Big Black Carpenter Ants to Large Sugar Ants.
Comprehensive Coverage Local Ants Control Service
We serve Seattle, Bellevue, Kirkland, Issaquah, Redmond, Sammamish, Mercer Island, Medina, Kent, Renton, Woodinville & Eastside, WA. No matter where you are, we’ve got you covered!
Professional Pest Control Solutions
Trust our experienced exterminators to tackle your ant problem with precision and care. We use advanced techniques and eco-friendly products to ensure long-lasting results.
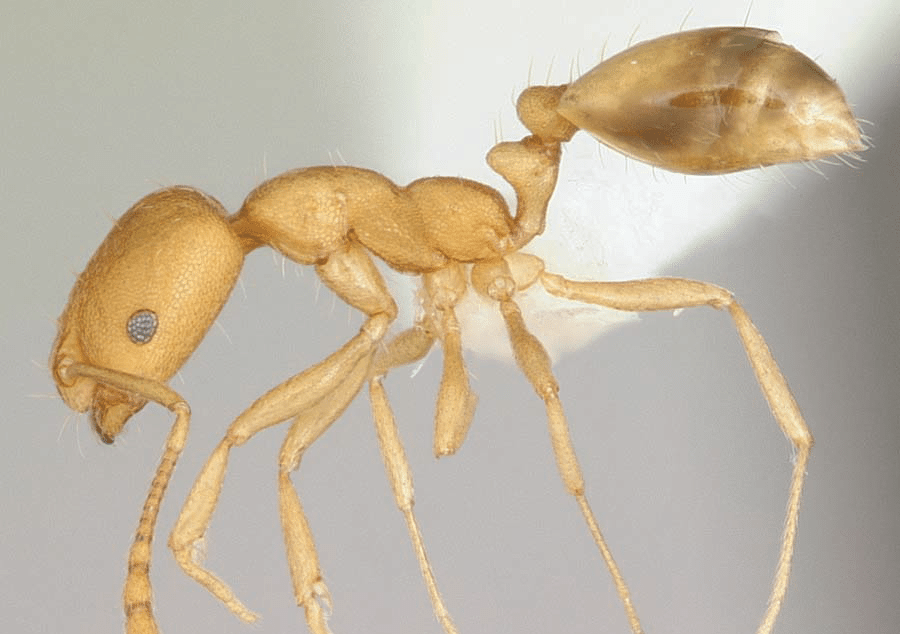
Understanding Carpenter Ants
Identification
Learn to identify big black carpenter ants and understand the signs of an infestation. With our expert guidance, you’ll know exactly what to look for and how to address the problem.
Damage Control
While carpenter ants don’t spread disease, they can wreak havoc on your property. Discover how they tunnel through wood and what you can do to protect your home or business.
Preventive Measures
From identifying moisture sources to sealing cracks, we’ll help you implement preventive measures to keep carpenter ants at bay. Don’t wait until it’s too late—take action now to safeguard your property.
Effective Ant Control Strategies
Targeted Treatments
Our pest control experts tailor their approach to your specific needs, ensuring maximum effectiveness and minimal disruption to your daily life.
Professional Equipment
We use state-of-the-art equipment and proven techniques to eliminate ants at their source. Say goodbye to ant colonies with our expert extermination services.
Long-Term Relief
Don’t settle for temporary solutions. Our goal is to provide you with long-term relief from ant infestations, so you can enjoy peace of mind knowing your property is protected.
FAQs About Ant Control Extermination
How Much Does It Cost to Hire a Carpenter Ant Exterminator?
Our pricing is competitive and transparent. Contact us for a free quote tailored to your specific needs.
Who Are the Best Ant Exterminators Near Me?
We pride ourselves on being the top-rated exterminators in the Seattle area. Our customer reviews speak for our expertise and commitment.
What Are the Best Services for Getting Rid of Carpenter Ants?
Our comprehensive services include inspection, targeted treatments, and preventive measures to ensure complete eradication of carpenter ants.
How Effective Are Professional Ant Extermination Services?
Professional services are highly effective because we understand ant behavior and use advanced methods to eliminate them at the source.
Can You Provide Emergency Ant Extermination?
Yes, we offer emergency services to address urgent ant infestations. Contact us immediately for prompt assistance.
What Methods Do Exterminators Use to Eliminate Carpenter Ants?
We use a combination of baiting, spraying, and dusting techniques tailored to your specific infestation.
Are Your Ant Control Treatments Safe for Pets and Children?
Absolutely. We use eco-friendly and pet-safe products to ensure the safety of your loved ones.
How Soon Can You Come to Treat a Carpenter Ant Infestation?
We offer same-day and next-day appointments to address your pest control needs promptly.
Do You Offer Eco-Friendly Ant Extermination Options?
Yes, we are committed to using environmentally friendly products and methods.
How Long Does It Take to Get Rid of Carpenter Ants Completely?
Depending on the severity of the infestation, complete eradication can take a few days to a couple of weeks.
Can You Prevent Future Ant Infestations?
Yes, our preventive measures include sealing entry points and addressing conditions conducive to ant infestations.
What Guarantees Do You Offer with Your Ant Extermination Services?
We offer a satisfaction guarantee and follow-up visits to ensure the problem is completely resolved.
Do You Provide Residential and Commercial Ant Control Services?
Yes, we cater to both residential and commercial clients, providing customized solutions for all types of properties.
Are There Any Additional Costs for Ant Extermination?
Our pricing is straightforward with no hidden fees. We provide a detailed quote before starting any work.
Do You Offer a Free Inspection for Carpenter Ant Problems?
Yes, we offer free inspections to assess the extent of the infestation and provide an accurate estimate.
Take Control of Your Ant Problem Today!
Don’t let ants ruin your home or business. Contact us now for expert ant extermination services and reclaim your space. With our help, you can say goodbye to ants for good and enjoy a pest-free environment. Let’s work together to make your property a place where ants are no longer welcome
 Workers are 4 to 4.5 mm long yellow in color. When crushed, they produce a lemon scent that is often described as citronella. When moisture ants move indoors, they often nest in wood that is moisture damaged. They frequently find damaged wood in areas like bath traps. They sometimes nest inside walls where there is a plumbing leak. There have been cases of these ants nesting in damp soil in crawlspaces. In these situations, the workers made mounds of excavated soil in the crawl space.
Workers are 4 to 4.5 mm long yellow in color. When crushed, they produce a lemon scent that is often described as citronella. When moisture ants move indoors, they often nest in wood that is moisture damaged. They frequently find damaged wood in areas like bath traps. They sometimes nest inside walls where there is a plumbing leak. There have been cases of these ants nesting in damp soil in crawlspaces. In these situations, the workers made mounds of excavated soil in the crawl space.
 Odorous House Ants
Odorous House Ants
Odorous house ants Sugar Ants can be very annoying as they frequently establish trails in your house along kitchen counters, cabinets, sinks, baseboards in their search for food. They can also be difficult to eradicate, since there can be several (or many) queens in several locations, the workers can all trail together regardless of their home colonies, the colonies frequently move from place to place, both inside outside.

Pavement Ants
Sidewalk ants, or pavement ants, are familiar to everyone. They are commonly seen during summer months on driveways, patio slabs, walkways. They will sometimes be seen pushing piles of sand other debris from cracks from along slab edges. There are many different species, of different size appearance.
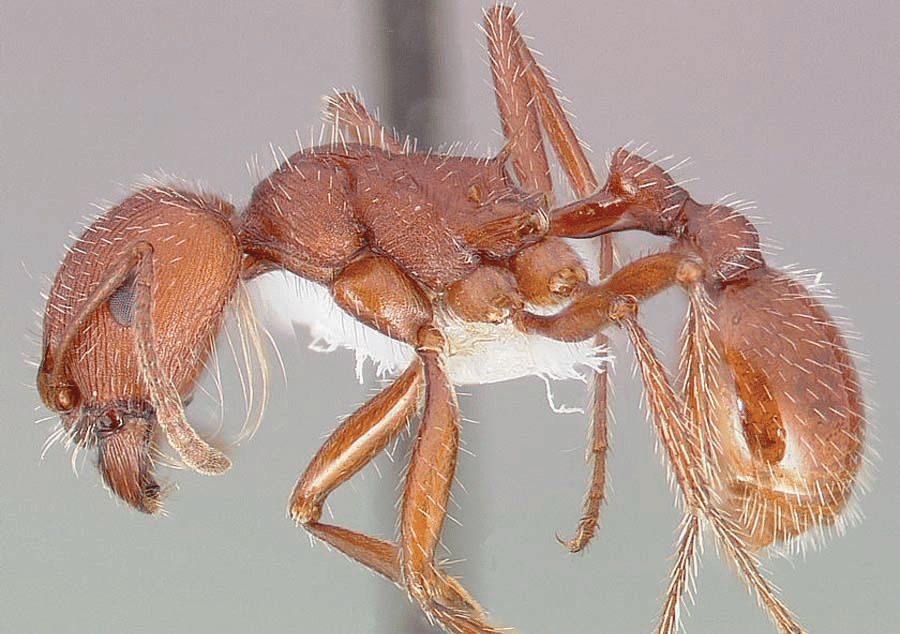
Thatch ants are a large black ants sometimes confused with carpenter ants. They have a distinctive red head, which carpenter ants do not. Primarily an outside ant, they will occasionally invade structures. Most species of thatching ants are bicolored red or black .A few are all black. They are medium to large ants, averaging from 4–8 mm (3/16–5/16 inch) long, with a notch or depression on the top of the thorax when viewed from the side. They are polymorphic, that is, the workers vary in size within the same colony. Their reproductive swarms (winged males queens leaving the colony) occur in late summer to early fall.
Pharaoh ant infests almost all areas of a building where food is available infests many areas where food is not commonly found. Pharaoh ants have a wide preference in the types of food consumed. In infested areas, if sweet, fatty, or oily foods are left uncovered for only a short period of time, one can likely find a trail of Pharaoh ants to the food. As a consequence, they cause much food to be discarded due to contamination. Also called, miscalled, sugar ants, grease ants, kitchen ants, and house ants.
The red harvester ants can be aggressive. They deliver a painful sting. Sometimes, the stings of harvester ants can cause allergic reactions, especially to those sensitive to their venom. Aside from their powerful stings, harvester ants also bite viciously
Velvety tree ants make their nest in the crooks of trees. Depending on the location, they nest in oaks, sycamores, cottonwoods, pines. They also nest in the soil under rocks and inside logs or stumps. Colonies are usually very large. Normally the entire colony nests in the same place. However, sometimes there are satellite colonies the workers move back forth between the nests.
Velvety tree ants eat honeydew, nectar, insects. They tend small insects, like aphids, because they produce honeydew. It is common to see velvety tree ant workers moving around in lines or trails on the trunks of trees. They often use tree limbs branches to enter homes other structures.